- Asian session review: yen weakness
Market news
Asian session review: yen weakness
The yen fell against the US dollar. A certain pressure on the yen has had the dramatic revision of the forecasts for GDP growth and inflation by the Government of Japan. Explaining this decision, the Government pointed to the increase in uncertainty about the global economy, weak domestic consumption and sluggish investment companies. Now it is expected that in the current fiscal year ending March 30, GDP growth adjusted for inflation will be 0.9%. Earlier this year, GDP growth is expected at 1.7%. The forecast for inflation was reduced to 0.4% versus 1.2% previously. The Government also stated that in 2017 fiscal year forecasts GDP growth of 1.2% and a rise in inflation to 1.4%.
Pound, from the beginning of the trading session, strengthened against the US dollar caused by Gbp/Jpy cross rise and profit taking before BOE meeting later today. At its meeting on Thursday the Bank of England may cut interest rates to a new record low and introduce quantitative easing, to protect the economy from the earlier decision to leave the EU. On Tuesday, the head of the Bank of England Governor Mark Carney said that any negative consequences for the UK economy Brexit may force the central bank to act, reinforcing hopes for additional stimulus measures.
The Australian dollar has strengthened since the beginning of trading after the release of positive data on inflation expectations in July. However, in the course of trading the Australian currency began to fall on to the negative data on the labor market in Australia.
The level of unemployment in Australia rose to 5.8% in June, slightly above the previous value of 5.7%, and coincided with the forecast of economists. The growth rate indicates a lack of momentum of the labor market in the country. As a result, this leads to a weakening of the national economy.
In a report the Australian Bureau of Statistics say, the unemployment rate in June was the highest since February that increased the likelihood of lowering interest rates by the Reserve Bank of Australia at a meeting early next month.
Despite the rise in unemployment, the number of jobs in June increased by 7.9 thousand vs 10 000 expected. The number of jobs increased full-time by 38 400 and the number of jobs part-time decreased by 30 600. The proportion of the economically active population in June rose to 64.9% from 64.8% in May, the forecast assumes that it will amount to 64.8%.
In July, inflation expectations for consumer prices in Australia, published by the Melbourne Institute, increased by 3.7%, which is higher than the previous value of 3.5%. This indicator reflects the expectations of consumers with regard to future inflation over the next 12 months. The higher the expectations, the more they will produce a significant effect on the probability of RBA rate moves.
There are strong expectations in the market as to whether the RBA will lower rates in August, when the central bank will be able to get acquainted with for the second quarter inflation data.
The last time the rate decreased in May, when the RBA reacted to data showing very weak inflation in the first quarter.
Now RBA rate is at a record low of 1.75%, while still space for its decrease. In its decision to change the interest rate, the RBA will follow from the fact that expectations of low inflation is not entrenched.
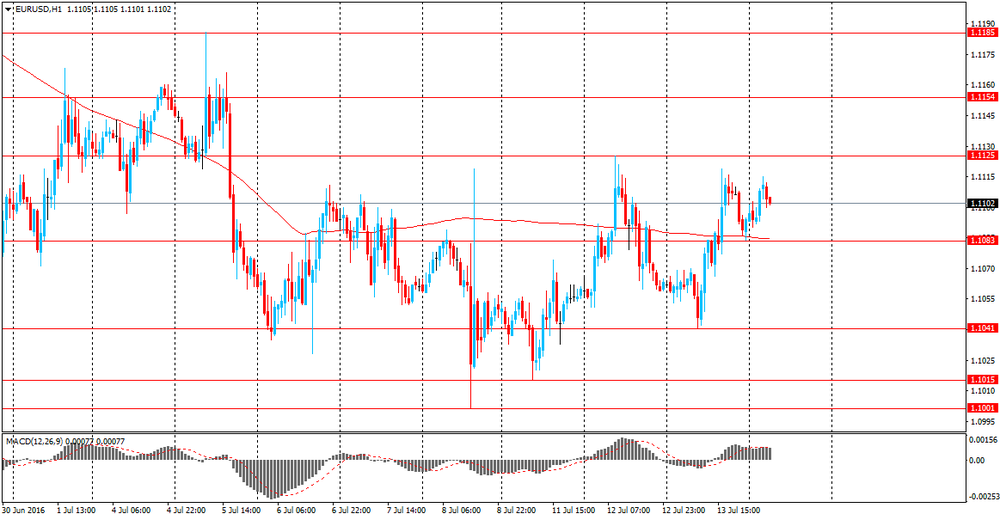
EUR / USD: during the Asian session, the pair is trading in the $ 1.1090-1.1120 range.
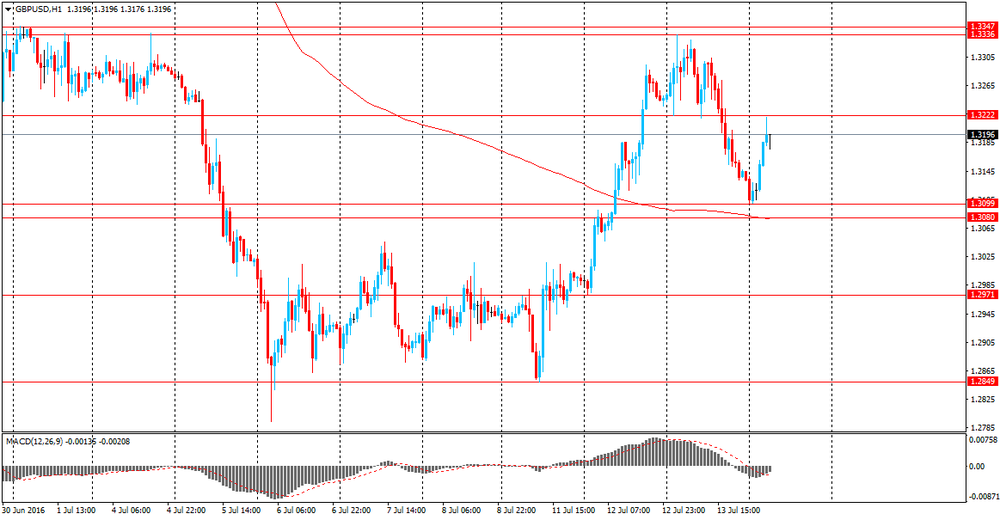
GBP / USD: during the Asian session, the pair is trading in the $ 1.3100-1.3235 range.
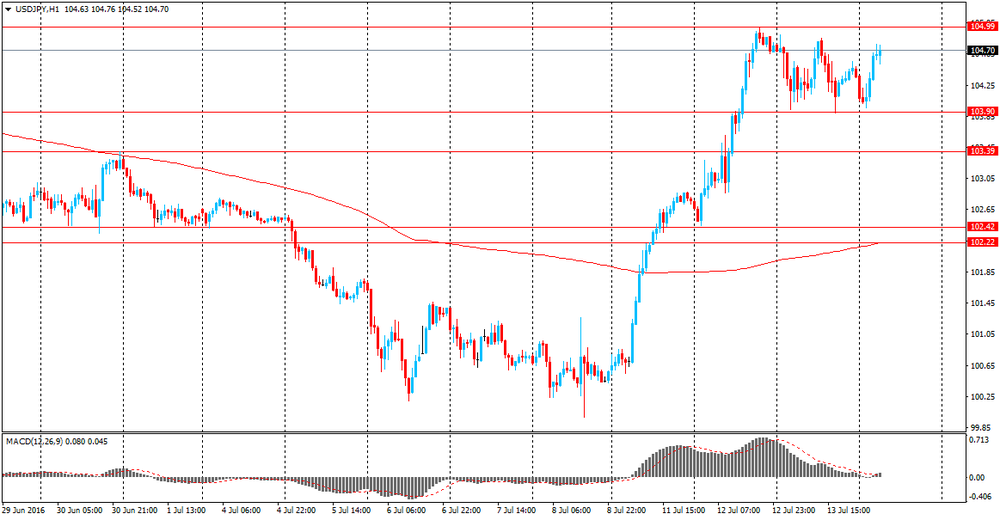
USD / JPY: during the Asian session, the pair was trading in Y103.95-105.40 range.