- Gold holds steady as markets await US CPI data
Market news
Gold holds steady as markets await US CPI data
- Gold price hovers around $2,180.60, steadying as traders anticipate February's CPI release.
- Core inflation expectations set to influence the US Dollar and potentially bolster Gold's position.
- Following Powell's testimony, Gold’s near breakthrough to $2,200 underlined XAU’s price sensitivity to Fed policy and inflation trends.
Gold prices were virtually unchanged late in the North American session with traders bracing for the release of February’s US Consumer Price Index (CPI) data, which is estimated to stay unchanged for headline figures. Core data is foreseen cooling down, which would weigh on the US Dollar and boost XAU/USD. At the time of writing, Gold price trades at $2,180.60, almost flat.
Last week, Gold price printed an all-time high of $2,195.15, shy of cracking the $2,200 figure following US Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell's testimony at the US Congress, in which he acknowledged that inflation is heading lower. Powell noted that eventually, the Fed would begin to ease policy but emphasized that the central bank remains data-dependent. Despite saying the US central bank is close to feeling confident that inflation is edging lower, the Fed Chair said they’re in no rush to cut borrowing costs.
Daily digest market movers: Gold’s last leg up sponsored by weak US NFP data
- The US labor market is cooling down despite printing solid gains in February compared to “downward revised” figures from January. After two months of net revisions, the US jobs market totaled a loss of -167,000 jobs compared with initial prints, which sparked a reaction from interest rate futures traders.
- According to the CME FedWatch Tool, expectations for a May rate cut remain low at 22%, but the odds are at 69% for June.
- February US CPI is expected to rise from 0.3% to 0.4% MoM and remain unchanged at 3.1% YoY.
- Core CPI is estimated to drop from 0.4% to 0.3% MoM and from 3.9% to 3.7% YoY.
- Federal Reserve officials last week expressed that they remain data-dependent and want to feel secure that inflation is sustainably trending toward the Fed’s 2% goal. Therefore, Tuesday’s inflation report would be relevant, as a jump in prices could trigger a U-turn in XAU/USD prices.
- XAU/USD is being capped by US Treasury bond yield recovery as the 10-year benchmark note rate gained two basis points at 4.094%.
Technical analysis: Gold stays firm near all-time highs near $2,180
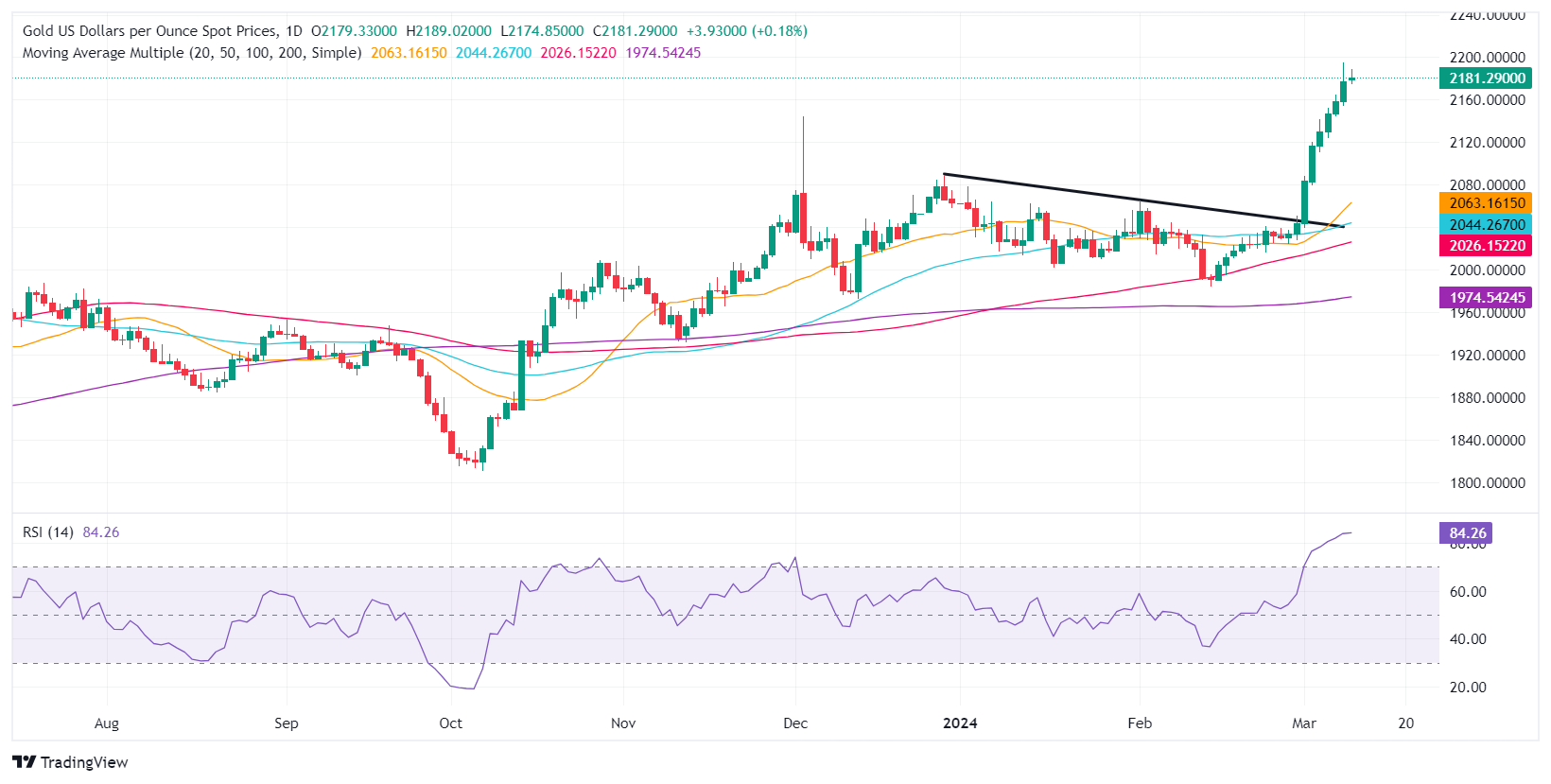
Gold’s rally appears overextended after extending toward the $2,180.00 figure. Even though the Relative Strength Index (RSI) is overbought above the 80 level, RSI’s slope aims up, suggesting that buyers remain in charge. If buyers push the XAU/USD price above the ATH at $2,195.15, that could open the door to testing $2,200.00.
On the flip side, if XAU/USD falls below March’s 8 low of $2,154.17, a drop toward the $2,150.00 figure is on the cards. Further support is seen at $2,100.00, ahead of the December 28 high at $2,088.48 and the February 1 high at $2,065.60.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.