Noticias del mercado
-
22:19
U.S. stocks retreated for a second day
U.S. stocks retreated for a second day, with investors anxious about corporate profits as Wal-Mart Stores Inc. predicted earnings will decline next year and quarterly results from JPMorgan Chase & Co. disappointed.
Wal-Mart's tumble sent equities lower after shares had fluctuated in early trading. The S&P 500 has lost momentum after its strongest week since December as investors look to earnings season for a better gauge on the outlook for corporate profits. The index has gained 3.9 percent this month, and is up 6.8 percent from an August selloff closing low as it fights back from the worst quarter since 2011.
Analysts project profits for S&P 500 members dropped 7.2 percent in the third quarter. Goldman Sachs Group Inc., Citigroup Inc. and UnitedHealth Group Inc. are among 16 companies in the index due to report results on Thursday.
Asian and European shares slipped today after a report showed China's factory gate deflation extended a record stretch of declines while inflation moderated. Weak imports data out of China helped send the S&P 500 lower yesterday.
U.S. data today showed retail sales in September rose less than forecast as Americans increased their savings, while the prior month was weaker than previously reported. Sluggish sales may raise concern about whether the staying power of consumer spending, which accounts for about 70 percent of the economy, at a time overseas demand is also cooling. A separate report showed falling energy costs damped wholesale inflation, as the producer price index decreased the most since January.
Federal Reserve officials last month left interest rates unchanged, opting to monitor the risk that China's slowdown could spill over to the U.S. After today's data from both China and the U.S., traders are now pricing in a 29 percent chance the central bank raises rates this year, while odds of a March increase are about 49 percent, down from 62 percent on Monday.
Fed Governor Daniel Tarullo told CNBC yesterday that he doesn't currently favor raising rates in 2015. That lines him up with fellow Governor Lael Brainard, who made the case on Monday for patience, and diverges from the majority of Federal Open Market Committee members including Chair Janet Yellen.
The central bank's Beige Book report on regional economic conditions released today showed the economy grew modestly with little inflation pressure from mid-August to early October as a strong dollar weighed on manufacturing and tourism. Six of the 12 Fed districts called the expansion "modest," while three reported "moderate" growth.
-
21:00
DJIA 16905.24 -176.65 -1.03%, NASDAQ 4782.38 -14.23 -0.30%, S&P 500 1992.37 -11.32 -0.56%
-
18:46
WSE: Session Results
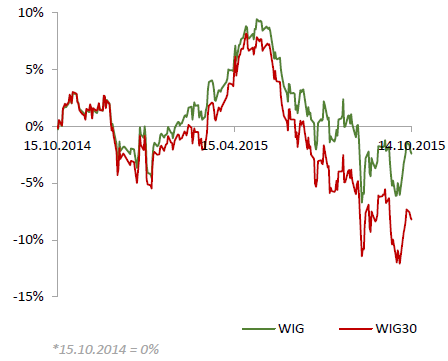
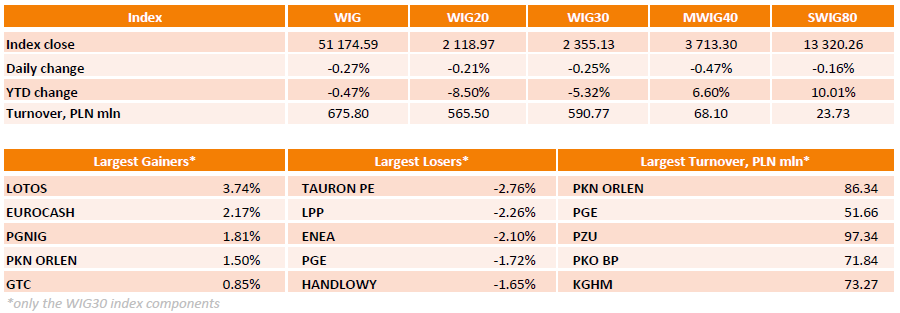
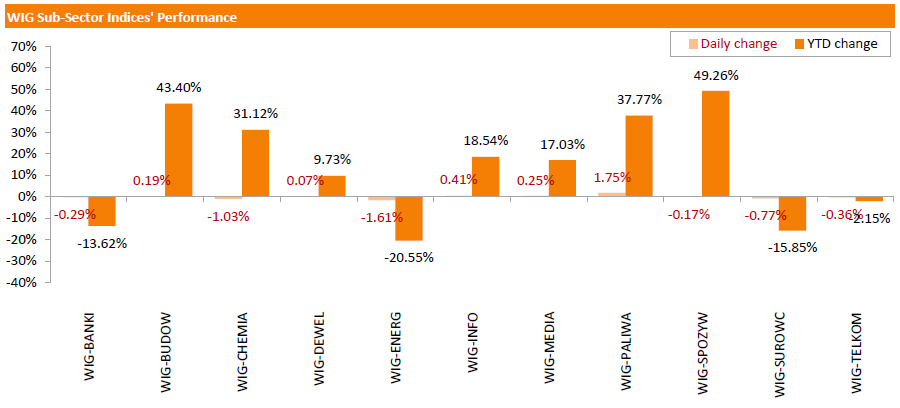
Polish equity market closed lower on Wednesday. The broad measure, the WIG index, lost 0.27%. Sector performance within the WIG Index was mixed. Oil and gas sector (+1.75%) was best performer, while utilities (-1.61%) recorded the worst result.
The large-cap benchmark, the WIG30 Index, fell by 0.25%. Within the index components, TAURON PE (WSE: TPE) was the worst-performing name, tumbling by 2.76% on news that Poland plans a share swap with the company to help finance its investment plans, including investments in the coal mining sector. The other notable losers were LPP (WSE: LPP) and ENEA (WSE: ENA), plunging 2.26% and 2.1% respectively. On the other side of the ledger, oil and gas sector names led the advancers, with LOTOS (WSE: LTS), PGNIG (WSE: PGN) and PKN ORLEN (WSE: PKN) rebounding by 1.5%-3.74% after yesterday's sharp declines. EUROCASH (WSE: EUR) also was among outperformers, gaining 2.17%.
-
18:00
European stocks close: stocks closed lower as the Chinese inflation data weighed
Stock indices lower as the Chinese inflation data weighed. The Chinese National Bureau of Statistics released its consumer and producer price inflation data for China on Wednesday. The Chinese consumer price index (CPI) rose at annual rate of 1.6% in September, missing expectations for a 1.8% increase, after a 2.0% gain in August.
The Chinese producer price index (PPI) dropped 5.9% in September, in line with expectations, after a 5.9% decline in August. It was the biggest decline since 2009.
European Central Bank (ECB) Executive Board Member Yves Mersch said in an interview with the Asian Banker on Wednesday that the central bank's asset-buying programme was successful.
Meanwhile, the economic data from the Eurozone was weaker than expected. Eurostat released its industrial production data for the Eurozone on Wednesday. Industrial production in the Eurozone declined 0.5% in August, in line with expectations, after a 0.8% gain in July. July's figure was revised up from a 0.6% rise.
The decrease was driven by declines in energy, non-durable consumer goods and capital output. Energy output dropped 3.0% in August, non-durable consumer goods were down 0.1%, while capital goods output fell by 1.0%.
On a yearly basis, Eurozone's industrial production gained 0.9% in August, exceeding expectations for a 1.8% rise, after a 1.7% increase in July. July's figure was revised down from a 1.9% gain.
The increase was driven by rises in durable and non-durable consumer goods and capital goods. Durable consumer goods climbed by 4.5% in August from a year ago, capital goods rose by 2.8%, while non-durable consumer goods gained by 0.1%.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) released its labour market data on Wednesday. The U.K. unemployment rate fell to 5.4% in the June to August quarter from 5.5% in the May to July quarter. It was the lowest reading since the second quarter of 2008.
Analysts had expected the unemployment rate to remain unchanged at 5.5%.
U.K. unemployment in the June to August period dropped by 79,000 to 1.7 million from the previous quarter.
Average weekly earnings, excluding bonuses, climbed by 2.8% in the June to August quarter, missing expectations for a 3.0% rise, after a 2.9% gain in the May to June quarter.
Average weekly earnings, including bonuses, rose by 3.0% in the June to August quarter, missing expectations for a gain of 3.1%, after a 2.9% increase in the May to June quarter.
The Bank of England monitors closely the wages growth it considers when to start hiking its interest rate.
Indexes on the close:
Name Price Change Change %
FTSE 100 6,269.61 -72.67 -1.15%
DAX 9,915.85 -116.97 -1.17%
CAC 40 4,609.03 -34.35 -0.74%
-
17:21
Wall Street. Major U.S. stock-indexes fell
Major U.S. stock-indexes fell on Wednesday as investors assessed earnings from major U.S. banks and health care stocks bounced back. Fresh economic data from China, however, appeared to limit gains - consumer inflation in the world's second-biggest economy cooled more than expected in September. While the health of China's economy continues to remain a concern, investors are focusing on company results.
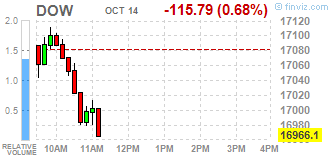
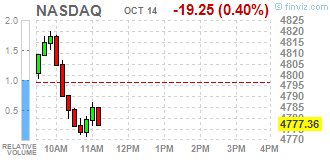
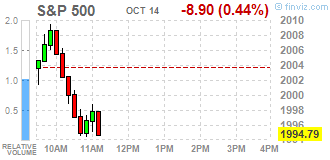
Dow stocks mixed (17 in negative area, 13 in positive). Top looser - Wal-Mart Stores Inc. (WMT, -9.25%). Top gainer - E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company (DD, +0.88%).
S&P index sectors mixed. Top looser - Services (-1.1%). Top gainer - Utilities (+0,6%).
At the moment:
Dow 16906.00 -67.00 -0.39%
S&P 500 1989.50 -4.50 -0.23%
Nasdaq 100 4331.00 -10.25 -0.24%
10 Year yield 2,00% -0,06
Oil 46.32 -0.34 -0.73%
Gold 1176.90 +11.50 +0.99%
-
16:50
Employment rate in the OECD area remains unchanged at 66.1% in the second quarter
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) released its employment rate for the second quarter on Wednesday. The employment rate in the OECD area remained unchanged at 66.1% in the second quarter.
The employment rate in the Eurozone was up 0.1% to 64.3% in the second quarter, the employment rate in the United Kingdom fell by 0.1% to 72.5%, while the rate in the United States climbed 0.1% to 68.7%.
Greece's employment rate climbed by 0.9% to 50.7% in the second quarter, while the employment rate in Germany declined by 0.3% to 73.7%.
-
16:32
U.S. business inventories are flat in August
The U.S. Commerce Department released the business inventories data on Wednesday. The U.S. business inventories were flat in August, missing expectations for a 0.1% rise, after a flat reading in July. July's figure was revised down from a 0.1% increase.
Retail inventories climbed 0.3% in August, wholesale inventories were up 0.1%, while manufacturing inventories fell 0.3%.
Business sales decreased 0.6% in August, while retail sales decreased 0.1%.
The business inventories/sales ratio climbed to 1.37 months in August from 1.36 months in July. The business inventories /sales ratio is a measure of how long it would take to clear shelves.
-
15:48
German government cuts its 2015 growth forecast
The German government cut its 2015 growth forecast to 1.7% on Wednesday, down from its April forecast of a 1.8% rise. The government said that the downward revision was driven by the slowdown in the Chinese economy and in other emerging economies.
The German economy is expected to expand 1.8% next year.
"The German economy is continuing to grow. It remains on track despite the subdued outlook for the global economy with weaker growth in China and commodity-rich emerging markets," German Economy Minister Sigmar Gabriel said.
German Economy Ministry said that private consumption will be the main contributor to growth this year. The ministry revised its private consumption forecasts for 2015 and 2016. The private consumption is expected to increase by 1.7% in 2015, down from April estimate of a 2.0% gain, and 2.1% in 2016, up from April estimate of a 1.8% rise.
-
15:37
European Central Bank Executive Board Member Yves Mersch: the central bank’s asset-buying programme was successful
European Central Bank (ECB) Executive Board Member Yves Mersch said in an interview with the Asian Banker on Wednesday that the central bank's asset-buying programme was successful.
"We believe that our program has been successful. After all, we had increasing risks of deflation in Europe," he said.
-
15:35
U.S. Stocks open: Dow -0.15%, Nasdaq +0.08%, S&P -0.07%
-
15:26
Before the bell: S&P futures -0.09%, NASDAQ futures -0.06%
U.S. stock-index futures fluctuated.
Global Stocks:
Nikkei 17,891 -343.74 -1.89%
Hang Seng 22,439.91 -160.55 -0.71%
Shanghai Composite 3,262.08 -31.15 -0.95%
FTSE 6,303 -39.28 -0.62%
CAC 4,629.57 -13.81 -0.30%
DAX 9,969.33 -63.49 -0.63%
Crude oil $46.77 (+0.24%)
Gold $1172.50 (+0.58%)
-
15:11
U.S. producer price falls 0.5% in September
The U.S. Commerce Department released the producer price index figures on Wednesday. The U.S. producer price index declined 0.5% in September, missing expectations for a 0.2% decline, after a flat rise in August.
On a yearly basis, the producer price index decreased 1.1% in September, missing forecasts of a 0.7% decline, after a 0.8% fall in August.
A stronger U.S. dollar and low oil prices still weigh on inflation.
Services prices were down 0.4% in September, while prices for goods declined 1.2%.
Food prices decreased by 0.8% in September, while energy sales declined 5.9%.
The producer price index excluding food and energy fell 0.3% in September, missing expectations for a 0.1% gain, after a 0.3% increase in August.
On a yearly basis, the producer price index excluding food and energy climbed 0.8% in September, missing forecasts of a 1.2% increase, after a 0.9% rise in August.
These figures could mean that the Fed will not start raising its interest rate this year.
-
14:59
Wall Street. Stocks before the bell
(company / ticker / price / change, % / volume)
Barrick Gold Corporation, NYSE
ABX
7.67
2.82%
15.5K
Freeport-McMoRan Copper & Gold Inc., NYSE
FCX
12.89
1.26%
8.9K
McDonald's Corp
MCD
104.00
0.60%
3.0K
Tesla Motors, Inc., NASDAQ
TSLA
220.05
0.36%
1.6K
Pfizer Inc
PFE
33.05
0.21%
3.2K
ALCOA INC.
AA
10.05
0.20%
4.6K
Yandex N.V., NASDAQ
YNDX
12.78
0.20%
0.5K
Home Depot Inc
HD
121.80
0.16%
0.2K
International Paper Company
IP
42.05
0.05%
0.1K
Boeing Co
BA
140.35
0.04%
1.6K
Wal-Mart Stores Inc
WMT
66.75
0.03%
1.5K
The Coca-Cola Co
KO
41.66
0.02%
0.6K
General Motors Company, NYSE
GM
33.13
0.00%
0.2K
Starbucks Corporation, NASDAQ
SBUX
60.16
0.00%
0.5K
Facebook, Inc.
FB
94.10
-0.02%
4.0K
Google Inc.
GOOG
652.05
-0.04%
1.5K
General Electric Co
GE
27.85
-0.07%
7.6K
Johnson & Johnson
JNJ
95.35
-0.10%
1.6K
Cisco Systems Inc
CSCO
27.81
-0.14%
0.1K
AT&T Inc
T
33.17
-0.15%
2.2K
Chevron Corp
CVX
88.25
-0.15%
84.6K
Microsoft Corp
MSFT
46.82
-0.15%
2.0K
Amazon.com Inc., NASDAQ
AMZN
548.00
-0.16%
2.9K
Walt Disney Co
DIS
106.40
-0.18%
0.2K
Goldman Sachs
GS
180.56
-0.23%
2.6K
Ford Motor Co.
F
14.89
-0.33%
9.8K
Yahoo! Inc., NASDAQ
YHOO
32.20
-0.43%
16.7K
Citigroup Inc., NYSE
C
50.95
-0.51%
39.0K
Apple Inc.
AAPL
111.00
-0.71%
230.6K
Twitter, Inc., NYSE
TWTR
28.68
-1.31%
108.1K
JPMorgan Chase and Co
JPM
60.60
-1.54%
145.2K
Intel Corp
INTC
31.25
-2.47%
196.4K
-
14:53
U.S. retail sales increase 0.1% in September
The U.S. Commerce Department released the retail sales data on Wednesday. The U.S. retail sales climbed 0.1% in September, missing expectations for a 0.2% decrease, after a flat reading in August. August's figure was revised up from a 0.2% rise.
The increase was mainly driven by higher automobiles purchases. Automobiles and car parts sales rose 1.7% in September.
Retail sales excluding automobiles decreased 0.3% in September, missing forecasts of a 0.1% decline, after a 0.1% fall in August. August's figure was revised down from a 0.3% increase.
Sales at building material and garden equipment stores declined 0.3% in September and sales at furniture stores increased 0.6%.
Sales at clothing retailers were up 0.9% in September, while sales at service stations dropped 3.2%.
These figures could mean that the Fed will not start raising its interest rate this year.
-
14:46
Upgrades and downgrades before the market open
Upgrades:
Intel (INTC) upgraded to Buy from Hold at Summit Research; target $40
McDonald's (MCD) upgraded to Buy from Neutral at Cleveland Research
Downgrades:
Twitter (TWTR) downgraded to Mkt Perform from Mkt Outperform at JMP Securities
Other:
Intel (INTC) reiterated at Market Perform at Cowen; target raised to $34 from $33
Intel (INTC) reiterated at Outperform at Northland Capital; target raised to $39 from $37.50
Intel (INTC) reiterated at Sector Perform at RBC Capital Mkts; target raised to $34 from $33
-
14:27
Greek import prices drop 2.2% in August
The Hellenic Statistical Authority released its import prices data for Greece on Wednesday. Greek import prices fell 2.2% in August, after a 2.4% decline in July.
On a yearly basis, import prices dropped 12.8% in August, after a 11.5% decrease in July.
Import prices for energy plunged by 40.4% in August, while price for non-durable consumer goods declined by 0.7%.
Prices of capital goods rose 0.2% in August, while intermediate goods prices decreased 0.1%.
-
14:18
Westpac’ consumer confidence index for Australia rises 4.2% in October
Westpac Bank released its consumer confidence index for Australia on late Tuesday evening. The index climbed 4.2% in October, exceeding expectations for a 3.0% rise, after a 5.6% drop in September.
"There has been a very significant and unexpected boost to respondents' assessment of the state of the labour market which looks to be an even more significant result than the increase in the overall index," Westpac Chief Economist Bill Evans said.
-
13:52
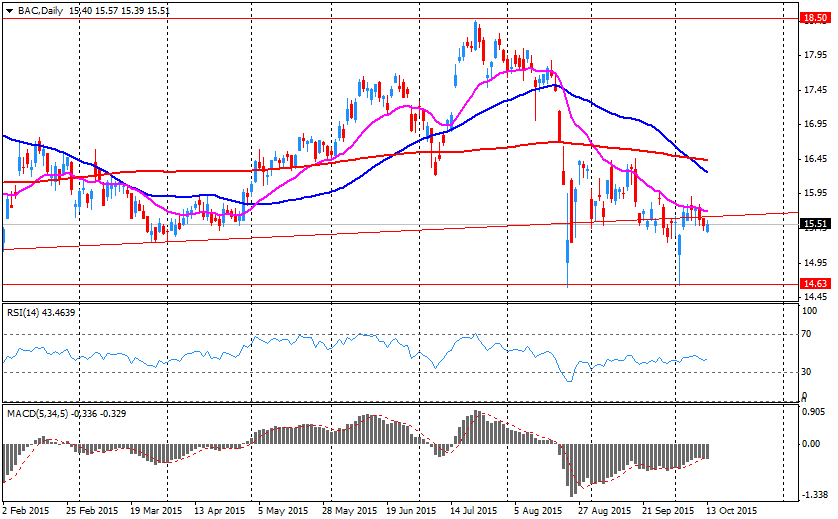
Company News: Bank of America (BAC) quarterly profit beats expectation
The company reported Q3 earnings of $0.37 per share versus net loss of $0.01 in the corresponding period of 2014. The EPS figure was better than analysts' consensus of $0.33.
The company's revenues fell by 2.4% y/y to $20.913 bln, generally in-line with consensus of $20.842 bln.
BAC rose to $15.88 (+2.32%) in pre-market trading.
-
12:00
European stock markets mid session: stocks traded lower on the Chinese inflation data
Stock indices traded lower on the Chinese inflation data. The Chinese National Bureau of Statistics released its consumer and producer price inflation data for China on Wednesday. The Chinese consumer price index (CPI) rose at annual rate of 1.6% in September, missing expectations for a 1.8% increase, after a 2.0% gain in August.
The Chinese producer price index (PPI) dropped 5.9% in September, in line with expectations, after a 5.9% decline in August. It was the biggest decline since 2009.
Meanwhile, the economic data from the Eurozone was weaker than expected. Eurostat released its industrial production data for the Eurozone on Wednesday. Industrial production in the Eurozone declined 0.5% in August, in line with expectations, after a 0.8% gain in July. July's figure was revised up from a 0.6% rise.
The decrease was driven by declines in energy, non-durable consumer goods and capital output. Energy output dropped 3.0% in August, non-durable consumer goods were down 0.1%, while capital goods output fell by 1.0%.
On a yearly basis, Eurozone's industrial production gained 0.9% in August, exceeding expectations for a 1.8% rise, after a 1.7% increase in July. July's figure was revised down from a 1.9% gain.
The increase was driven by rises in durable and non-durable consumer goods and capital goods. Durable consumer goods climbed by 4.5% in August from a year ago, capital goods rose by 2.8%, while non-durable consumer goods gained by 0.1%.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) released its labour market data on Wednesday. The U.K. unemployment rate fell to 5.4% in the June to August quarter from 5.5% in the May to July quarter. It was the lowest reading since the second quarter of 2008.
Analysts had expected the unemployment rate to remain unchanged at 5.5%.
U.K. unemployment in the June to August period dropped by 79,000 to 1.7 million from the previous quarter.
Average weekly earnings, excluding bonuses, climbed by 2.8% in the June to August quarter, missing expectations for a 3.0% rise, after a 2.9% gain in the May to June quarter.
Average weekly earnings, including bonuses, rose by 3.0% in the June to August quarter, missing expectations for a gain of 3.1%, after a 2.9% increase in the May to June quarter.
The Bank of England monitors closely the wages growth it considers when to start hiking its interest rate.
Current figures:
Name Price Change Change %
FTSE 100 6,292.49 -49.79 -0.79 %
DAX 9,924.3 -108.52 -1.08 %
CAC 40 4,606.96 -36.42 -0.78 %
-
11:43
Fed Governor Daniel Tarullo: it would not be appropriate to raise interest rates this year
Fed Governor Daniel Tarullo said in an interview with CNBC on Tuesday that it would not be appropriate to raise interest rates this year.
"I wouldn't expect it would be appropriate to raise rates," he said.
Tarullo added that he would like to see any signs that the inflation accelerates before to start raising interest rates.
"There have been a series of factors which, for some period of time, have kept inflation down, and that's why my own perspective is that one should watch to see some tangible evidence that allows one to develop that reasonable confidence that inflation will return to target," Fed governor said.
-
11:36
Final consumer price inflation in Spain declines 0.3% in September
The Spanish statistical office INE released its final consumer price inflation data on Wednesday. Consumer price inflation in Spain was down 0.3% in September, in line with preliminary reading, after a 0.3% fall in August.
On a yearly basis, consumer prices fell by 0.9% in September from a year ago, in line with preliminary reading, after a 0.4% decline in August.
The annual decline was mainly driven by a drop in the prices of housing and transport.
-
11:28
French consumer price inflation declines 0.4% in September
The French statistical office Insee released its consumer price inflation for France on Wednesday. The French consumer price inflation decreased 0.4% in September, after a 0.3% rise in August.
On a yearly basis, the consumer price index was flat in September, after a flat reading in August.
Fresh food prices rose 7.4% year-on-year in September, while petroleum products prices dropped by 14.3%.
-
11:23
ZEW Institute and Credit Suisse Group’s survey: Switzerland's economic sentiment index climbs to 18.3 points in October, the highest reading since March 2014
A survey by the ZEW Institute and Credit Suisse Group showed on Wednesday that Switzerland's economic sentiment index climbed to 18.3 points in October from 9.7 points in September. It was the highest reading since March 2014.
"The ZEW-CS Indicator for Switzerland continued its upward trend in October 2015," the ZEW said.
The current conditions rose to -5.3 points in October from -9.7 points in September.
-
11:13
Eurozone’s industrial production declines 0.5% in August
Eurostat released its industrial production data for the Eurozone on Wednesday. Industrial production in the Eurozone declined 0.5% in August, in line with expectations, after a 0.8% gain in July. July's figure was revised up from a 0.6% rise.
The decrease was driven by declines in energy, non-durable consumer goods and capital output. Energy output dropped 3.0% in August, non-durable consumer goods were down 0.1%, while capital goods output fell by 1.0%.
Intermediate goods increased by 0.2% in August, while durable consumer goods output climbed 2.3%.
On a yearly basis, Eurozone's industrial production gained 0.9% in August, exceeding expectations for a 1.8% rise, after a 1.7% increase in July. July's figure was revised down from a 1.9% gain.
The increase was driven by rises in durable and non-durable consumer goods and capital goods. Durable consumer goods climbed by 4.5% in August from a year ago, capital goods rose by 2.8%, while non-durable consumer goods gained by 0.1%.
Energy output was down by 1.6% in August from a year ago, while intermediate output declined by 0.6%.
-
11:01
U.K. unemployment rate declines to 5.4% in the June to August quarter
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) released its labour market data on Wednesday. The U.K. unemployment rate fell to 5.4% in the June to August quarter from 5.5% in the May to July quarter. It was the lowest reading since the second quarter of 2008.
Analysts had expected the unemployment rate to remain unchanged at 5.5%.
"Today's fall in unemployment has more than outstripped the recent rises, leaving unemployment at its lowest level since mid-2008. Meanwhile, employment continues to grow with the employment rate now at its highest since records began in 1971," ONS labour market statistician, Nick Palmer said.
The claimant count rose by 4,600 people in September, missing expectations for a decline by 2,100, after an increase of 1,200 people in August.
U.K. unemployment in the June to August period dropped by 79,000 to 1.7 million from the previous quarter.
Average weekly earnings, excluding bonuses, climbed by 2.8% in the June to August quarter, missing expectations for a 3.0% rise, after a 2.9% gain in the May to June quarter.
Average weekly earnings, including bonuses, rose by 3.0% in the June to August quarter, missing expectations for a gain of 3.1%, after a 2.9% increase in the May to June quarter.
The Bank of England monitors closely the wages growth it considers when to start hiking its interest rate.
-
10:49
BofA Merrill Lynch Fund Manager Survey: 47% of investors expect the Fed to start raising its interest rates this year
According to the BofA Merrill Lynch Fund Manager Survey, 47% of investors expect the Fed to start raising its interest rates this year, down from 58% in September. 209 investors were surveyed.
"As investors debate the timing of a rate hike, they should be anticipating a massive policy shift in the U.S., Europe and Japan from QE to fiscal stimulus in 2016," chief investment strategist at BofA Merrill Lynch Global Research, Michael Hartnett, said.
39% of investors said that China is the greatest "tail risk".
-
10:39
Bank of England's Monetary Policy Committee Member Gertjan Vlieghe: the economic developments abroad are main risks to the U.K. economy
The Bank of England's (BoE) Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) Member Gertjan Vlieghe said on Tuesday that the economic developments abroad are main risks to the U.K. economy.
"We absolutely have to take into account that we are operating in a global environment, which is adverse, so to speak, in that there are headwinds to growth," he said.
Vlieghe replaced David Miles in September.
-
10:27
Chinese consumer price index rises at annual rate of 1.6% in September
The Chinese National Bureau of Statistics released its consumer and producer price inflation data for China on Wednesday. The Chinese consumer price index (CPI) rose at annual rate of 1.6% in September, missing expectations for a 1.8% increase, after a 2.0% gain in August.
The inflation was driven by a rise in food prices. Food prices rose at an annual rate of 2.7% in September, while non-food prices increased 1.0%.
On a monthly basis, consumer price inflation increased 0.1% in September, after a 0.5% rise in August.
The Chinese producer price index (PPI) dropped 5.9% in September, in line with expectations, after a 5.9% decline in August. It was the biggest decline since 2009.
-
10:21
New Zealand’s government reaches its budget surplus for the first time since 2008
The New Zealand government reached its budget surplus in the fiscal year ending June 30. It was the first budget surplus since 2008. The budget surplus was driven by stronger-than-expected tax revenue.
Net debt was 25.2% of gross domestic product (GDP) in the fiscal year ending June 30, down from 25.6% from the last fiscal year.
Nominal GDP was NZ$240.6 billion in the fiscal year ending June 30, up 2.8% from the last fiscal year.
-
10:10
Reserve Bank of New Zealand Governor Graeme Wheeler: the further interest rate cut by the central bank is likely
Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) Governor Graeme Wheeler said on Wednesday that the further interest rate cut by the RBNZ is likely, but it will depend on the incoming data.
Next central bank's meeting is scheduled to be on October 29.
"We remain conscious of the impact that low interest rates can have on housing demand and its potential to feed into higher price inflation. It is important also to consider whether borrowing costs are constraining investment, and the need to have sufficient capacity to cut interest rates if the global economy slows significantly," he said.
Wheeler noted that the slowdown in the Chinese economy is a risk to the global economy.
"Any substantial depreciation in the RMB (Renminbi) would have serious implications for the world economy: it would risk triggering exchange rate adjustment among competitor economies - particularly in Asia, and would spread deflationary forces across the globe," RBNZ Governor said.
-
04:03
Nikkei 225 17,892.01 -342.73 -1.88 %, Hang Seng 22,381.58 -218.88 -0.97 %, Shanghai Composite 3,298.94 +5.71 +0.17 %
-
00:32
Stocks. Daily history for Sep Oct 13’2015:
(index / closing price / change items /% change)
Nikkei 225 18,234.74 -203.93 -1.11 %
Hang Seng 22,600.46 -130.47 -0.57 %
S&P/ASX 200 5,202.85 -30.01 -0.57 %
Shanghai Composite 3,293.64 +5.98 +0.18 %
FTSE 100 6,342.28 -28.90 -0.45 %
CAC 40 4,643.38 -45.32 -0.97 %
Xetra DAX 10,032.82 -87.01 -0.86 %
S&P 500 2,003.69 -13.77 -0.68 %
NASDAQ Composite 4,796.61 -42.03 -0.87 %
Dow Jones 17,081.89 -49.97 -0.29 %
-